
#DEFAULT CISCO MAC ADDRESS AGING TIME MAC#
You can control MAC address learning on an interface or VLAN to manage the available MAC address table space. Notice that port e0/6 is listed as Disabled-management.Ĩ02.By default, MAC address learning is enabled on all interfaces and VLANs and MAC address aging is set to 300 seconds on a Cisco switch. The command is issued in the example below, followed by the show int command. One other option for securing a switch is to disable unused ports using the shutdown command. Maximum mac address count for this secure portĬisco1912(config-if)#port secure max-mac-count 4 This command is issued from interface configuration mode.Ĭisco1912(config-if)#port secure max-mac-count ? To configure a port such that it only allows a certain number of connections, use the port secure max-mac-count command.
The maximum number of connections that can be specified per port is 132. While one system per port might be optimal, this isn’t always possible based on cost factors. For example, let’s say that you want to avoid there ever being more than 4 systems connected on any given port.
#DEFAULT CISCO MAC ADDRESS AGING TIME SERIES#
The Cisco 1900 series also includes a feature that allows you to control how many MAC addresses are allowed to be connected to a given switch port, without specifying individual MAC addresses as permanent entries. The example below shows how this setting can be changed from global configuration mode.Ĭisco1912(config)#mac-address-table aging-time ?Ĭisco1912(config)#mac-address-table aging-time 600 If a dynamic MAC address entry in the table isn’t heard from within 300 seconds, the entry is flushed. Notice that in order to add a permanent entry, you will need to supply both the MAC address of the system that will be connected, as well as the port to which this permanent entry applies. The mac-address-table command is used to add permanent entries to the MAC address table, as shown below.Ĭisco1912(config)#mac-address-table permanent ?Ĭisco1912(config)#mac-address-table permanent 0000.1234.5678 ?Ĭisco1912(config)#mac-address-table permanent 0000.1234.5678 e0/7 When a permanent entry is configured, only the MAC addresses entered into the table are capable of communicating via that port. Although this can sometimes be a great deal of work, it does make sense in cases where you want to be sure that unknown systems can’t just plug into a switch port (probably via a wall jack) and gain access to your network. Restricted Clear 802.1d restricted static addressĪ common way to implement security on a Layer 2 switch is by adding permanent MAC address entries to a switch port. Permanent Clear 802.1d permanent addresses This command has three options, including the ability to clear permanent, dynamic, and restricted entries. Number of restricted static addresses : 0Īddress Dest Interface Type Source Interface ListĠ000.1223.30A5Ğthernet 0/5 PermanentĚllĮntries can be cleared from a switch’s MAC address table by issuing the clear mac-address-table command. The table shows not only the MAC addresses of connected devices, but also the port number they are associated with, and whether these entries are dynamic or permanent. To view the MAC address table on a Cisco 1900, issue the show mac-address-table command. It is also possible to add permanent entries to the MAC address table, as we’ll see shortly. They will exist in the MAC table until the table is manually cleared, or until a certain host is not heard from for a certain period of time – the default is 300 seconds. These entries, which are added to the table automatically, are known as dynamic entries.
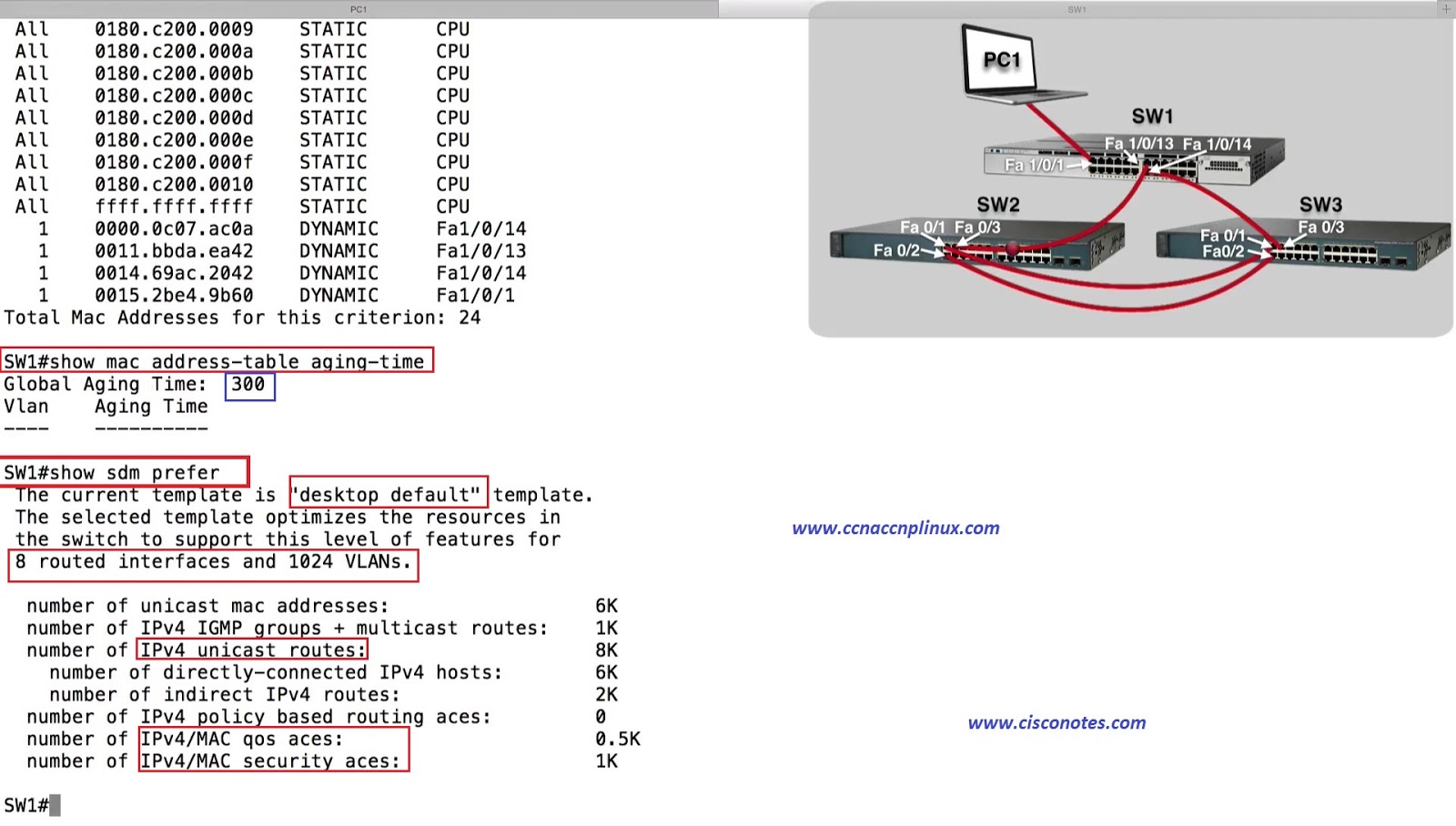
By default, a Catalyst 1900 switch can store up to 1024 entries in its MAC address table. This table is built as the switch inspects the source addresses of frames as they enter the switch from devices connected to a given port. A switch makes forwarding decisions based on the entries stored in its MAC address table.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
